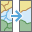
 The Dissolve Boundaries tool merges area features that either intersect or have the same field values.
The Dissolve Boundaries tool merges area features that either intersect or have the same field values.
Workflow diagram
Analysis using GeoAnalytics Tools
Analysis using GeoAnalytics Tools is run using distributed processing across multiple ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server machines and cores. GeoAnalytics Tools and standard feature analysis tools in ArcGIS Enterprise have different parameters and capabilities. To learn more about these differences, see Feature analysis tool differences.
Examples
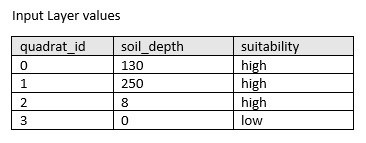
An agricultural development company sampled thousands of terrestrial quadrats across a county. The data includes a soil_depth field, and a suitability field. The suitability field was calculated by classifying soil_depth values into categories of low or high. The quadrats can be dissolved based on the suitability field to determine where the most expansive suitable area is located.
Usage notes
Specify the area feature layer you want to dissolve boundaries for using the Choose area layer whose boundaries will be dissolved parameter.
Use the Choose dissolve method parameter to define how boundaries are dissolved by selecting from one of two options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
Areas that overlap or are adjacent | Two or more areas whose boundaries overlap or who share a common boundary will be merged into one area. This is the default. |
Areas with the same field value | Areas will be merged into one area if they have the same field value. More than one field can be selected to merge areas. |
The Allow multipart features option determines whether the results will include multipart or single part features. A multipart feature is defined as one feature that is broken up into noncontiguous parts. For example, the state of Hawaii could be considered a multipart feature because its separate geometric parts are classified as a single state. The following options are available when deciding to create multipart or single part output:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
False (unchecked) | Only single part features will be created in the output. This is the default. |
True (checked) | The output will create any multipart features if applicable. |
The following table outlines how the multipart parameter operates for each dissolve option:
| Dissolve method | Multipart is false (default) | Multipart is true |
|---|---|---|
Areas that overlap or are adjacent (default) | 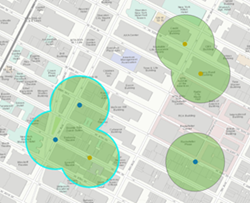 Three features are created when all values are dissolved and multipart is false. Only overlapping features are dissolved. This is the same as the standard analysis tool's Dissolve option. This is the default. | 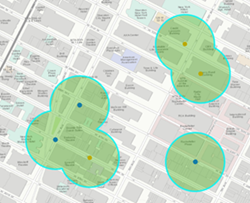 One feature is created when all values are dissolved and multipart is true. When you select this option, the result will always be one feature. |
| Areas with the same field value | 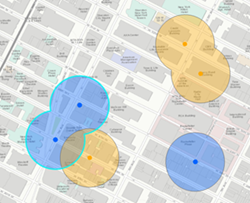 Four features are created when the dissolve is applied based on the field (here, the field is the color of input points). Only overlapping features with the same value of the specified fields are dissolved. | 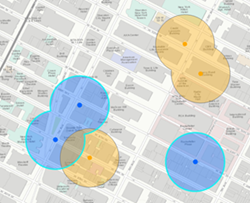 Two features are created when the dissolve is applied based on the field (here, the field is the color of input points) and multiparts are allowed. Values with the same field value will always be a single feature. |
If Use current map extent is checked, only the features that are visible within the current map extent will be analyzed. If unchecked, all input features in the input layer will be analyzed, even if they are outside the current map extent.
Limitations
Inputs to the Dissolve Boundaries tool must be area features.
How Dissolve Boundaries Works
Calculations
Optionally, you can calculate one or more statistics for the dissolved areas by using the Add statistics parameter. The following soil depth example outlines how statistics are calculated for dissolved features with a suitability value of high.
| Numeric Statistic | Calculated Results |
|---|---|
Count | Count of: |
Sum | |
Minimum | Minimum of: |
Maximum | Maximum of: |
Average | |
Variance | |
Standard Deviation | |
| String Statistic | Calculated Results |
|---|---|
Count | ["high", "high", "high"] = 3 |
Any | = "high" |
Note:
The count statistic (for strings and numeric fields) counts the number of nonempty values. The count of [0, 1, 10, 5, null, 6] = 5. The count of [Primary, Primary, Secondary, null] = 3.
ArcGIS API for Python example
The Dissolve Boundaries tool is available through ArcGIS API for Python.
This example dissolves boundaries of soil areas in Nebraska if they have the same solubility. For dissolved features, it calculates the sum of the quadrat area, the mean soil depth, and an example of the quadrat description.# Import the required ArcGIS API for Python modules
import arcgis
from arcgis.gis import GIS
from arcgis.geoanalytics import manage_data
# Connect to your ArcGIS Enterprise portal and check that GeoAnalytics is supported
portal = GIS("https://myportal.domain.com/portal", "gis_publisher", "my_password", verify_cert=False)
if not portal.geoanalytics.is_supported():
print("Quitting, GeoAnalytics is not supported")
exit(1)
# Find the big data file share dataset you're interested in using for analysis
search_result = portal.content.search("", "Big Data File Share")
# Find the Feature Layer containing the features you want to dissolve and apply a filter
dissolve_features_search = portal.content.search("study_areas", "Feature Layer")
dissolve_features = dissolve_features_search[0].layers[0]
dissolve_features.filter = "region = 'Nebraska'"
# Define the fields containing the values used to dissolve features
dissolve_fields = "soil_suitability"
# Define the statistics to calculate for dissolved areas
summary_fields = [{"statisticType" : "Sum", "onStatisticField" : "quadrat_area_km2"},
{"statisticType" : "Mean", "onStatisticField" : "soil_depth_cm"},
{"statisticType" : "Any", "onStatisticField" : "quadrat_desc"}]
# Set the tool environment settings
arcgis.env.out_spatial_reference = 3310
arcgis.env.output_datastore= "relational"
arcgis.env.defaultAggregations= True
# Run the tool Dissolve Boundaries
dissolve_result = manage_data.dissolve_boundaries(input_layer = dissolve_features,
dissolve_fields = dissolve_fields,
summary_fields = summary_fields,
multipart = True
output_name = "Soil_Suitability_dissolved")
# Visualize the tool results if you are running Python in a Jupyter Notebook
processed_map = portal.map('Nebraska')
processed_map.add_layer(dissolve_result)
processed_map
Similar tools
Use Dissolve Boundaries when you want to aggregate intersecting areas or areas with the same field value into a single area. Other tools may be useful in solving similar but slightly different problems.
Map Viewer analysis tools
Create buffered areas and dissolve buffers that intersect or have the same field value using the ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server tool Create Buffers.
Combine two layers into a single layer using Intersect or Erase methods using the ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server tool Overlay Layers.
ArcGIS Desktop analysis tools
To run this tool from ArcGIS Pro, your active portal must be Enterprise 10.7 or later. You must sign in using an account that has privileges to perform GeoAnalytics Feature Analysis.
Perform similar dissolve operations in ArcGIS Pro with the Dissolve geoprocessing tool.