ArcGIS Pipeline Referencing keeps event measures in alignment with LRS route edits. You can configure event behavior rules to define how event measures are updated for each type of route edit.
What is event behavior?
Events are located along a route in a linear referencing system (LRS) using a location reference (for example, measure distance down a route). Because location is based on the route length, changes in the length have a direct impact on how the events will be located and how they are rendered on a map. The impact of the changes to the route have on events is called event behavior.
Pipeline Referencing supports multiple ways to locate your event on a route, such as measure on route, reference offset from intersection, stations, feature offsets, offset from another event, or x,y coordinates.
Below is an example of a route being realigned. This route has a line event and a point event located along the route. After a route is edited, the events are updated using the event behavior rules.
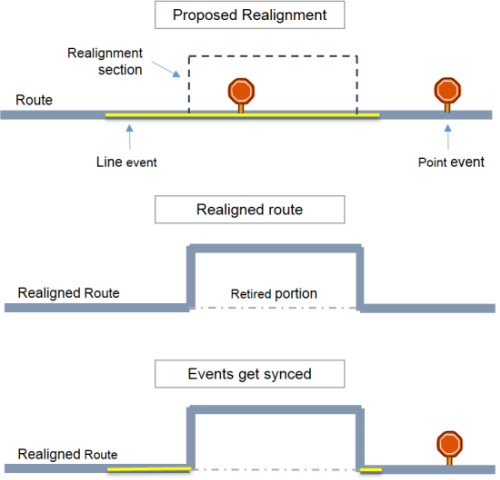
Types of event behavior rules
When an LRS route is edited, behavior rules are applied to the events. By providing the event behavior rules, you decide what the event does when the route changes: preserve location or preserve measure.
| Event behavior rules | Description |
|---|---|
| Stay Put | Preserves the geographic location of the event; measures may change. |
Move | Preserves the measure(s) of the event; geographic location may change. |
| Retire | Preserves both measure and geographic location; event is retired. |
Stay Put
The Stay Put rule preserves the geographic location of the event. When the route is modified, events retain their x,y coordinates. This means event measures will change whenever it is necessary to retain the location.
With Stay Put event behavior, events downstream of an edit section retain the location. The line events that intersect the edit section will be split into two or more events, so the portion not affected by the route edit will retain its location. Events that are completely contained within the edit section are retired.
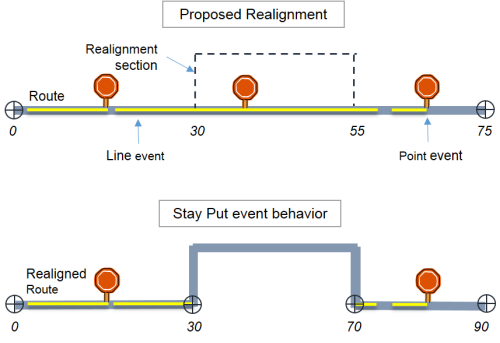
In the above example, the upstream events that did not intersect the realignment did not change. The line event that spans the realignment section gets split into two parts, and the original event is retired. The point event that falls inside the realignment section is retired. The downstream events retain the x,y location.
The table below shows how the Stay Put event behavior updates events for each edit activity.
| Activity | Events upstream | Events within edit section | Events downstream |
|---|---|---|---|
Extend Route | No action | Shape regenerated. | Measure(s) adjusted to retain x,y if recalibrate downstream selected as an option |
Calibrate Route, Reverse Route | Measure(s) adjusted to retain x,y | Measure(s) adjusted to retain x,y. | Measure(s) adjusted to retain x,y |
Realign Route, Realign Overlapping Route | Up to closest upstream calibration point; measure(s) adjusted to retain x,y if needed | Retire event; line events crossing edit section will be split and original event retired. | Measure(s) adjusted to retain x,y if recalibrate downstream selected as an option |
Retire Route, Reassign Route | No action | Retire event; line events crossing edit section will be split and original event retired. | Measure(s) adjusted to retain x,y if recalibrate downstream selected as an option |
Move
The Move rule preserves the measure(s) of the event. When a route is modified, events retain their measure values. This means x,y coordinates may change.
For example, with Move event behavior, events downstream of a realignment retain the measure, although the location along the route changes.
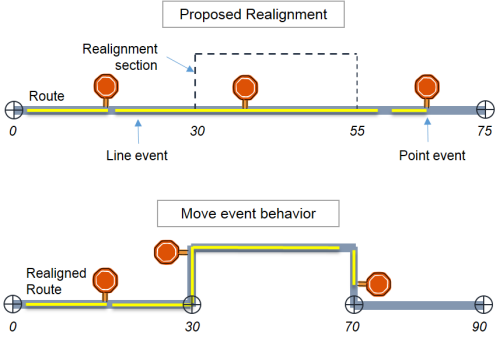
In the above example, events in the realignment section and downstream preserve the measures and their shape is updated per the new route shape.
The table below shows how the Move event behavior updates events for each edit activity.
| Activity | Events upstream | Events within edit section | Events downstream |
|---|---|---|---|
Extend Route | No action | Shape regenerated | Shape regenerated if recalibrate downstream selected as an option |
Calibrate Route, Reverse Route | Shape regenerated if needed | Shape regenerated | Shape regenerated if needed |
Realign Route, Realign Overlapping Route, Retire Route, or Reassign Route | Shape regenerated if needed | Shape regenerated | Shape regenerated if recalibrate downstream selected as an option |
Retire
The Retire event behavior preserves both measure and location. When you modify a route, the system flags the event as retired by changing its To Date value to the effective date of the edit if the event is in an impacted region of the route.
The event's measure(s) does not change, but the event will no longer be displayed in the current alignment of the highway. If you want to see the event, you must set the event layer's temporal view date (TVD) to a date and time prior to the edit.
For more information about changing the time view, see Setting the time view for LRS data.
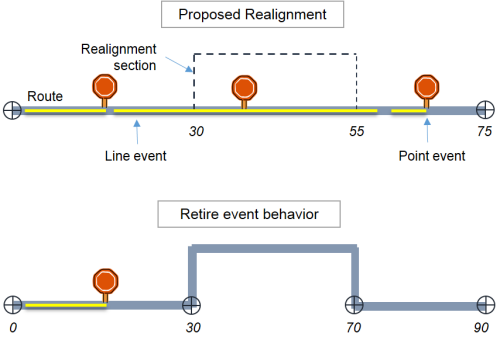
In the above example, the upstream events, where retaining the measure and location was possible, did not change. The line events that fall in the realignment section completely or partially are retired. The point event that falls inside the realignment section is retired. The downstream events are retired as well.
The table below shows how the Retire event behavior updates events for each edit activity.
| Activity | Events upstream | Events within edit section | Events downstream |
|---|---|---|---|
Extend Route | No action. | Retire event. | Retire event if recalibrate downstream is selected as an option. |
Calibrate Route, Reverse Route | Retire event. | Retire event. | Retire event. |
Realign Route, Realign Overlapping Route | Up to closest upstream calibration point; retire event if needed. | Retire event; line events crossing edit section will not be split. | Retire event if recalibrate downstream is selected as an option. |
Retire Route, Reassign Route | No action. | Retire event; line events crossing edit section will not be split. | Retire event if recalibrate downstream is selected as an option. |
Factors to consider
In addition to the above event behavior rules, there are a few other factors to consider to completely understand event behavior.
Recalibrate downstream
Route edits affect the calibration of the route, and during the edit activity, the Pipeline Referencing dialog box may ask you if you want to recalibrate downstream.
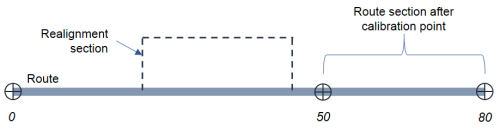
As shown in the above example, there are calibration points at measures 0, 50, and 80. You can choose to recalibrate downstream during realign activity. This will update the calibration of the route after the calibration point at measure 50 until the end of the route.
Due to recalibration, the event behavior is applied to the recalibrated section per the rule you set for Calibrate Route.
Application of event behavior
Event layers reside within the geodatabase that contains your ALRS. For more information, see Event types.
Events can have event behavior applied after each edit or a series of edits using the Apply Event Behavior geoprocessing tool. For more information, see Apply Event Behaviors.
Configuration of event behavior rules
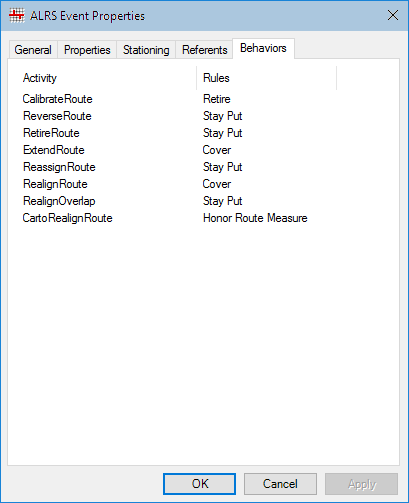
Event behavior is configured when you register events with the LRS Network. You can also reconfigure event behavior at any time by opening the event layer's properties.
During the process of registering events through the ALRS Event Setup wizard, you can set event behavior rules for each type of activity applied to the route.
Note:
Event behavior rules are not applied to X and Y offset events, Offset from an Event, and Offset from a Point Feature Class.
For more information about registering an event, see Registering an event within the ALRS geodatabase.