 The Summarize Attributes tool summarizes like field values to generate a summary table. The resulting layer displays the count of features that have been summarized, as well as any additional statistics that have been specified.
The Summarize Attributes tool summarizes like field values to generate a summary table. The resulting layer displays the count of features that have been summarized, as well as any additional statistics that have been specified.
Workflow diagram
Analysis using GeoAnalytics Tools
Analysis using GeoAnalytics Tools is run using distributed processing across multiple ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server machines and cores. GeoAnalytics Tools and standard feature analysis tools in ArcGIS Enterprise have different parameters and capabilities. To learn more about these differences, see Feature analysis tool differences.
Examples
Tornadoes and hurricanes are some of the most violent types of storms that occur in the United States. You want to know property damage and financial loss for tornadoes and hurricanes to compare how their impact differs. You have access to tornado and hurricane data across the United States in a single dataset, and you want to summarize all the information to see a summary of values for all hurricanes and a summary of values for all tornadoes. You can summarize your data using the type of storm to determine the statistics for each storm type.
Usage notes
Summarize Attributes is a tabular analysis tool, not spatial.
The most basic aggregations will calculate a count of the number of features that have been summarized. Statistics (count, sum, minimum, maximum, range, mean, standard deviation, and variance) can also be calculated on numerical fields, and statistics (count and any) can be calculated on string fields. The statistics will be calculated on each group separately.
You can specify one or more fields to summarize by or summarize all features. When you summarize by fields, statistics are calculated for each unique combination of attribute values.
The processing spatial reference and spatial reference of your input data will not affect your results.
If Use current map extent is checked, only the features that are visible within the current map extent will be analyzed. If unchecked, all input features in the input layer will be analyzed, even if they are outside the current map extent.
Limitations
Inputs may be a tabular layer or a layer with geometry (points, lines, or areas).
You can apply this tool to spatial data, and you will get a tabular result. You can join your results to spatial data using Join Features.
How Summarize Attributes works
Equations
Variance is calculated using the following equation: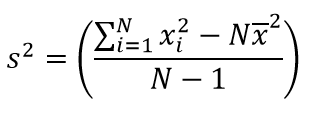

Standard deviation is calculated as the square root of the variance.
Calculations
Input layers are summarized into groups with matching field values. The results are tabular, so they cannot be visualized on your map.
The tables below illustrate the statistical calculations of a layer that is summarized using like values of fields. The VO2 field was used to calculate the numeric statistics (Count,Sum, Minimum, Maximum, Range, Mean, Standard Deviation, and Variance) for the layer. The Rating field was used to calculate the string statistics (Count and Any) for the layer.
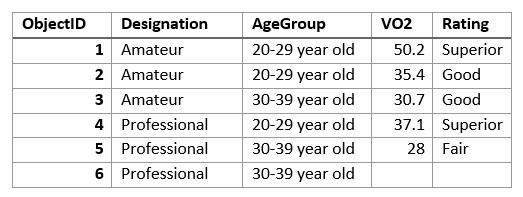
The table above was summarized on the field Designation, and the VO2 field was used to calculate the numeric statistics (Count,Sum, Minimum, Maximum, Range, Mean, Standard Deviation, and Variance) for the layer. The Rating field was used to calculate the string statistics (Count and Any) for the layer. This results is a table with two features, representing the distinct values of Designation.
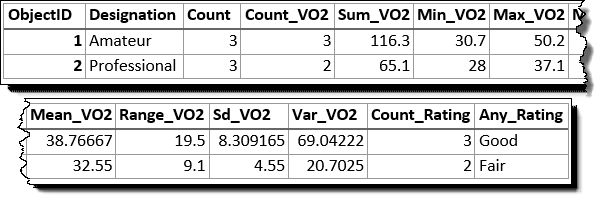
The following table represents what the first few fields look like when the layer is summarized using the Designation and Age Group fields. Statistics are calculated using the same methods as the previous example.
The count statistic (for strings and numeric fields) counts the number of nonnull values. The count of the following values equals 5: [0, 1, 10, 5, null, 6] = 5. The count of this set of values equals 3: [Primary, Primary, Secondary, null] = 3.
ArcGIS API for Python example
The Summarize Attributes tool is available through ArcGIS API for Python.
This example summarizes similar types of storms to find the sum of property damage.# Import the required ArcGIS API for Python modules
import arcgis
from arcgis.gis import GIS
from arcgis.geoanalytics import summarize_data
# Connect to your ArcGIS Enterprise portal and check that GeoAnalytics is supported
portal = GIS("https://myportal.domain.com/portal", "gis_publisher", "my_password", verify_cert=False)
if not portal.geoanalytics.is_supported():
print("Quitting, GeoAnalytics is not supported")
exit(1)
# Find the big data file share dataset you're interested in using for analysis
search_result = portal.content.search("", "Big Data File Share")
# Look through search results for a big data file share with the matching name
bd_file = next(x for x in search_result if x.title == "bigDataFileShares_NaturalDisaters")
# Look through the big data file share for Storms
storms = next(x for x in bd_file.layers if x.properties.name == "StormData")
# Set the tool environments
arcgis.env.verbose = True
arcgis.env.defaultAggregations = True
summaryStatistics = [{"statisticType" : "Sum", "onStatisticField" : "PropertyDamage"}]
summarized_result = summarize_data.summarize_attributes(input_layer = storms,
fields = "Storm_type",
summary_fields = summaryStatistics,
output_name = "summarized_storms")
# Visualize the tool results if you are running Python in a Jupyter Notebook
processed_map = portal.map('USA')
processed_map.add_layer(summarized_result)
processed_map
Similar tools
Use Summarize Attributes to summarize features with like values. Other tools may be useful in solving similar but slightly different problems.
Map Viewer analysis tools
If you are trying to summarize points, lines, or areas using different spatial relationships, use the GeoAnalytics Tools Join Features.
ArcGIS Desktop analysis tools
The GeoAnalytics Tools Summarize Attributes is available in ArcGIS Pro.
Summarize Attributes performs the functions of the Summary Statistics tool.