You can extend the functionality and capacity of the base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment with additional servers. Adding more server machines, be they on your premises or in the cloud, to your ArcGIS Enterprise deployment will help you make the most of the ArcGIS Server licensing roles.
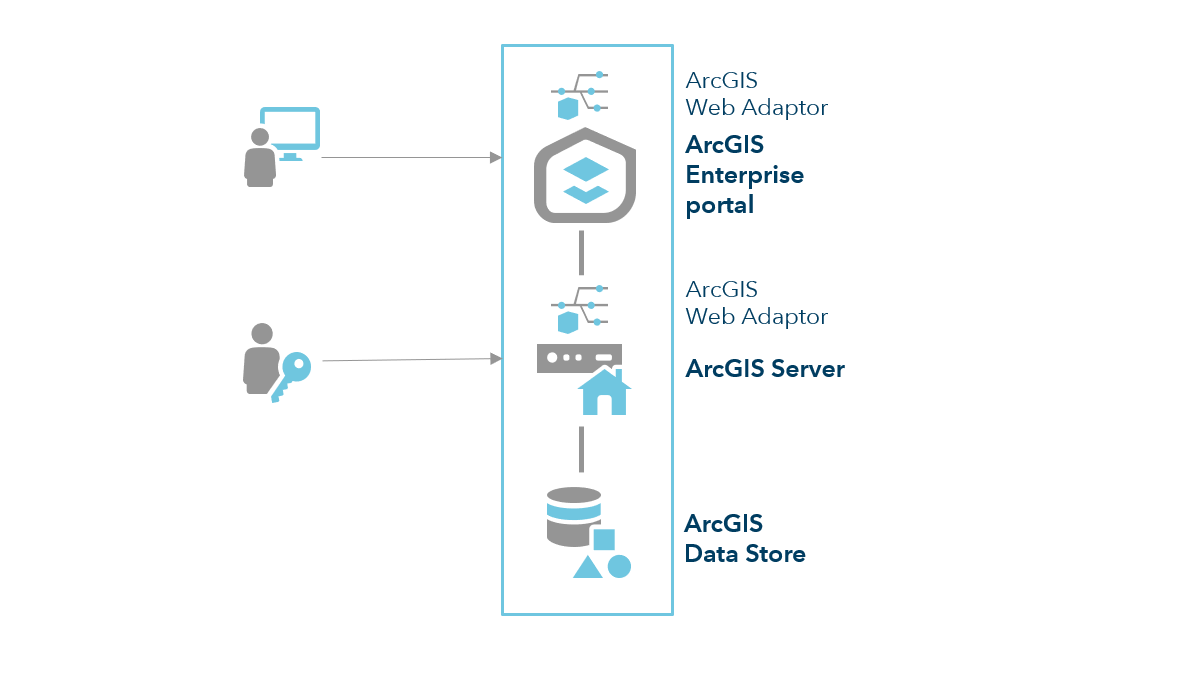
The base deployment of ArcGIS Enterprise comprises the following components:
- An ArcGIS Enterprise portal.
- ArcGIS Server, federated with the portal and designated as the portal's hosting server.
- ArcGIS Data Store for relational data, registered with the server as its managed database.
- Two instances of ArcGIS Web Adaptor - one configured with the portal and one with the server.
In this configuration, users access your web GIS resources through the portal website. Administrators and publishers can access ArcGIS Server directly for their purposes.
ArcGIS GIS Server
In the base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment, ArcGIS GIS Server acts in two distinct capacities:
- The hosting server that supports the overall Web GIS infrastructure.
- A general purpose GIS Server, where services can be published from ArcGIS Desktop that reference your own data sources, such as geodatabases.
Many organizations separate these functions into two distinct ArcGIS Server sites to improve the performance of their deployment.
In this configuration, an additional three-machine ArcGIS GIS Server site is federated with your ArcGIS Enterprise portal. This additional site provides dedicated mapping and visualization capabilities to your users. The number of machines in each site will be dictated by your specific needs for capacity and high availability.
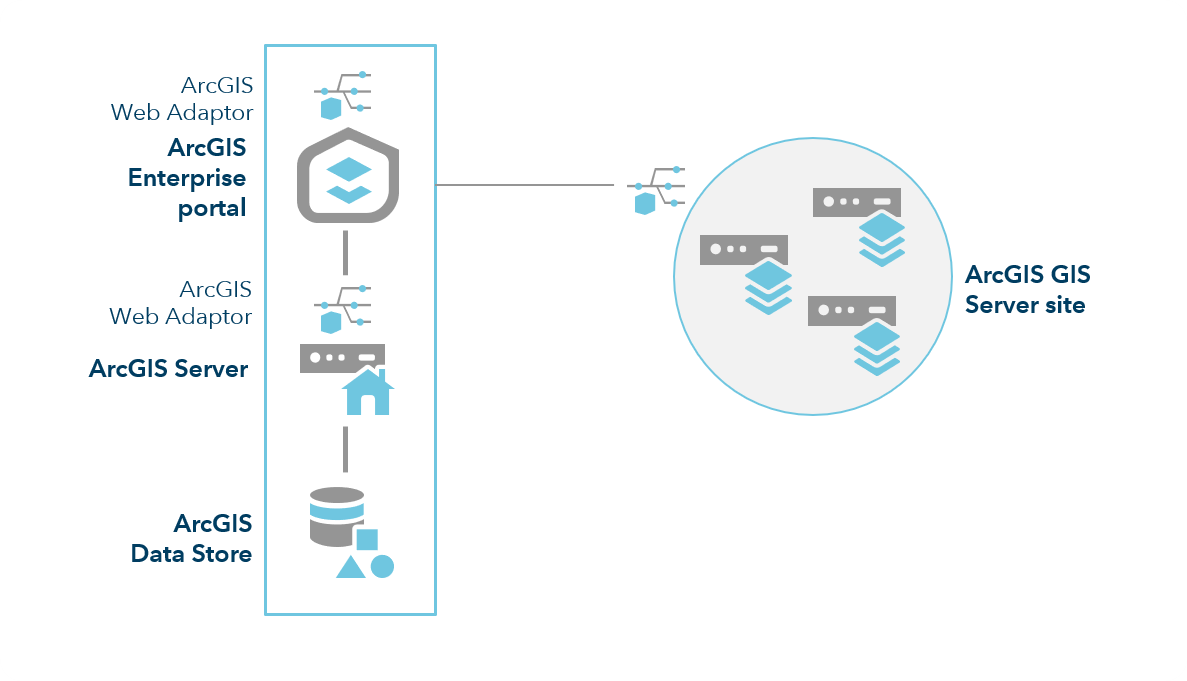
Each machine in the ArcGIS GIS Server site requires a minimum of 8 GB of memory, with more potentially required depending on the number of services published and their usage patterns.
ArcGIS Image Server
Image Server provides two primary capabilities: dynamic image services from mosaic datasets and raster analysis using distributed processing.
If you will only be using dynamic image services, the recommended deployment pattern is to add a dedicated ArcGIS Image Server site to the base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment.
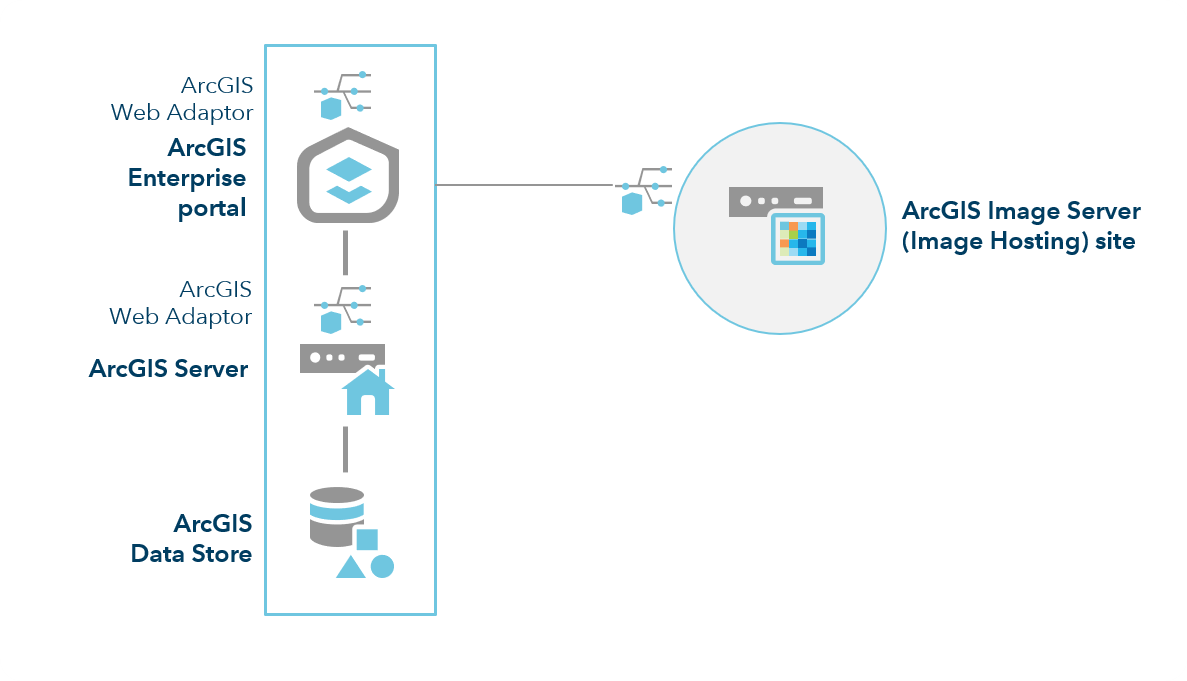
You can also federate additional ArcGIS Image Server sites to this deployment pattern as needed.
For deployments where raster analysis will regularly be performed on large datasets, to ensure that dynamic image services are not negatively impacted, you should use separate sites for raster analysis and dynamic image services.
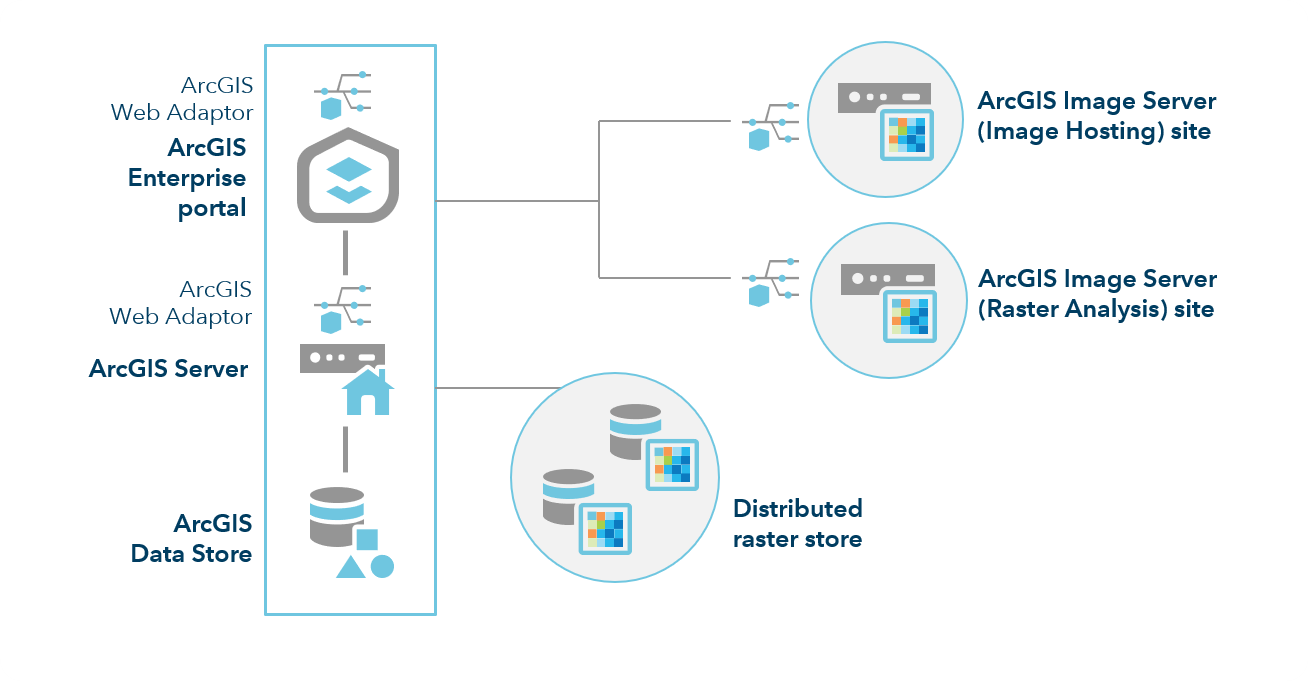
In such a deployment pattern, you should have a minimum of 8 GB of RAM per machine.
Configure and deploy ArcGIS Enterprise for raster analytics
Note:
You can only have one ArcGIS Image Server site dedicated to raster analytics in yourArcGIS Enterprise deployment. You can scale the site by adding more RAM or additional machines.ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server
To federate an ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server site to your base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment, you must also add an ArcGIS Data Store configured as a spatiotemporal big data store, installed on its own machine:
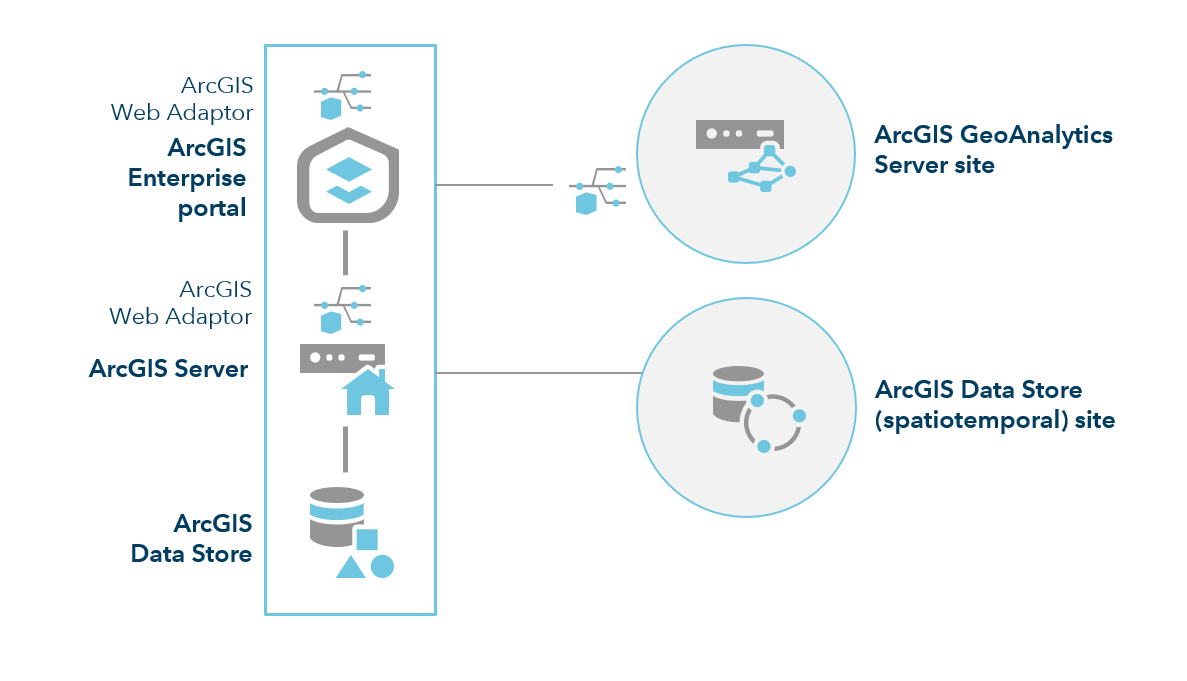
This deployment is appropriate for development and testing, as well as production use when there are no requirements for high availability. To learn about the minimum requirements on your GeoAnalytics Server and spatiotemporal big data store, see the best practices for GeoAnalytics topic..
Depending on the size of your data, and the analysis you are completing, you may need to add additional machines to your spatiotemporal big data store and ArcGIS GeoAnalytics Server site to accelerate your analysis. The diagrams below illustrate this deployment pattern.
Note:
You can only have oneGeoAnalytics Server site for your ArcGIS Enterprise deployment. You can scale the site by adding more RAM or additional machines. GeoAnalytics Server supports one machine and three-machine GeoAnalytics Server site configurations. To learn more about adding machines to your GeoAnalytics Server site, see Add machines to a GeoAnalytics site.The following diagram includes three machines for the spatiotemporal big data store registered with your hosting server, and a three-machine GeoAnalytics Serversite:
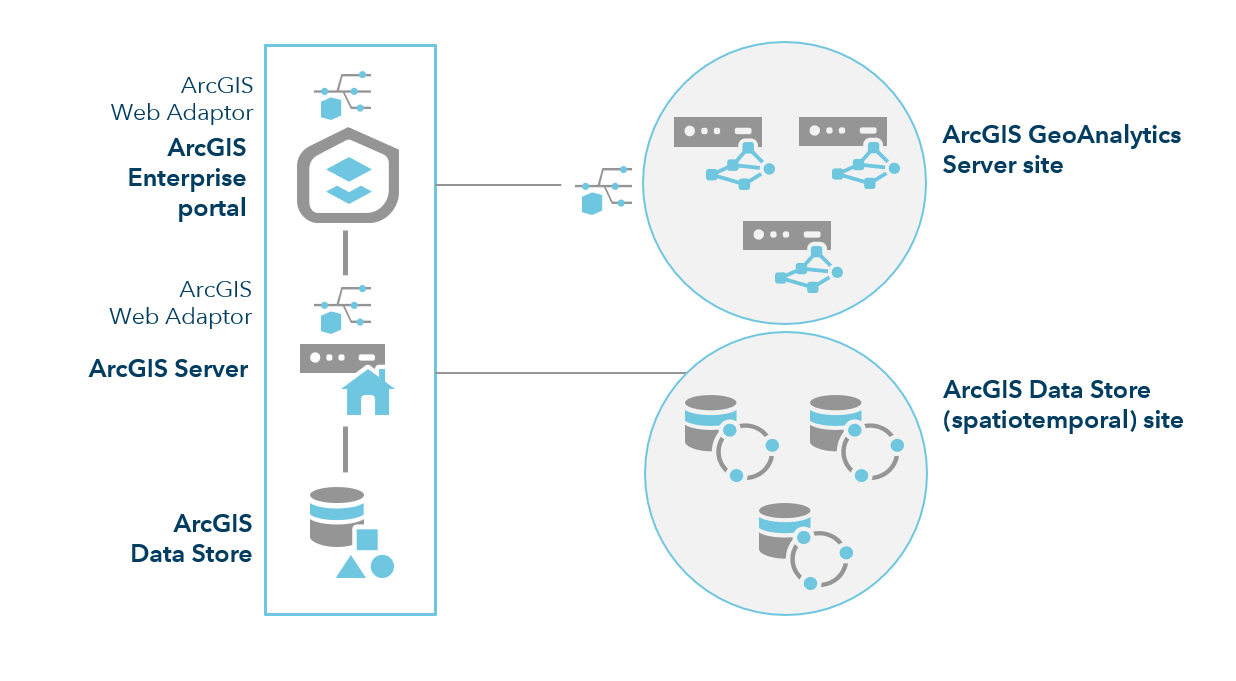
You must also ensure good I/O throughput from the input data sources configured with GeoAnalytics Server. This includes ensuring good throughput from remote file shares.
Learn more about planning, configuring, and modifying your GeoAnalytics Server site
ArcGIS GeoEvent Server
ArcGIS GeoEvent Server enables real-time event-based data streams from sensor networks, whether stationary, mobile, or an Internet of Things (IoT), to be integrated as data sources in your enterprise GIS.
The ideal number and configuration of ArcGIS GeoEvent Server instances for your deployment depends wholly on your data stream or streams — their event velocity and the data size of each event. A single instance of ArcGIS GeoEvent Server can process a stream with a volume of up to 6,000 events per second if the event data size only includes a few data fields and a point. The same hardware and software configuration may only be able to process 2,000 events per second if each event includes several dozen data fields and a many-sided polygon.
Learn more about system requirements for ArcGIS GeoEvent Server
A minimal setup adds a single-machine site with the ArcGIS GeoEvent Server licensing role to the existing base ArcGIS Enterprise deployment.
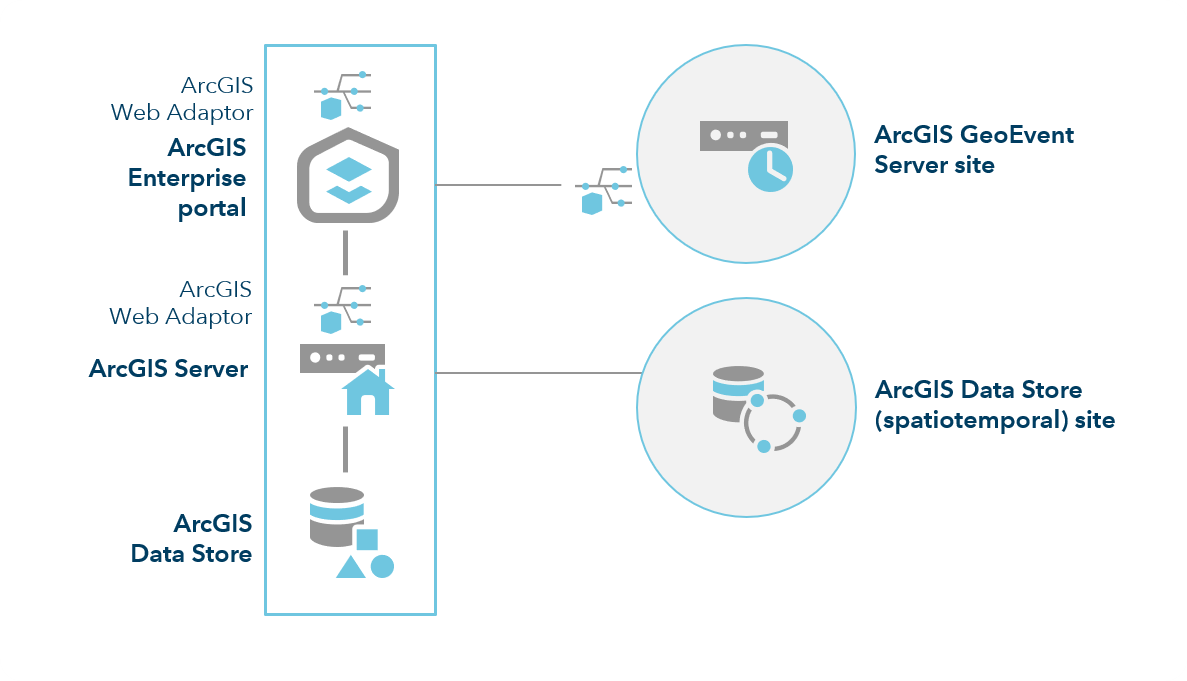
Note:
The configuration above illustrates a three-node spatiotemporal big data store registered with your hosting server. Incorporating a three-node spatiotemporal big data store enables high-velocity and large-volume archiving of event data processed by ArcGIS GeoEvent Server. The relational data store type in ArcGIS Data Store can handle data streams with an event volume below 200 events per second.
If your real-time sensor network includes multiple data streams, each with a moderate event volume and velocity, you should configure multiple single-machine ArcGIS GeoEvent Server sites, each dedicated to specific real-time data streams. The diagram below depicts such a configuration, with three independent ArcGIS GeoEvent Server instances, each in their own ArcGIS Server site.
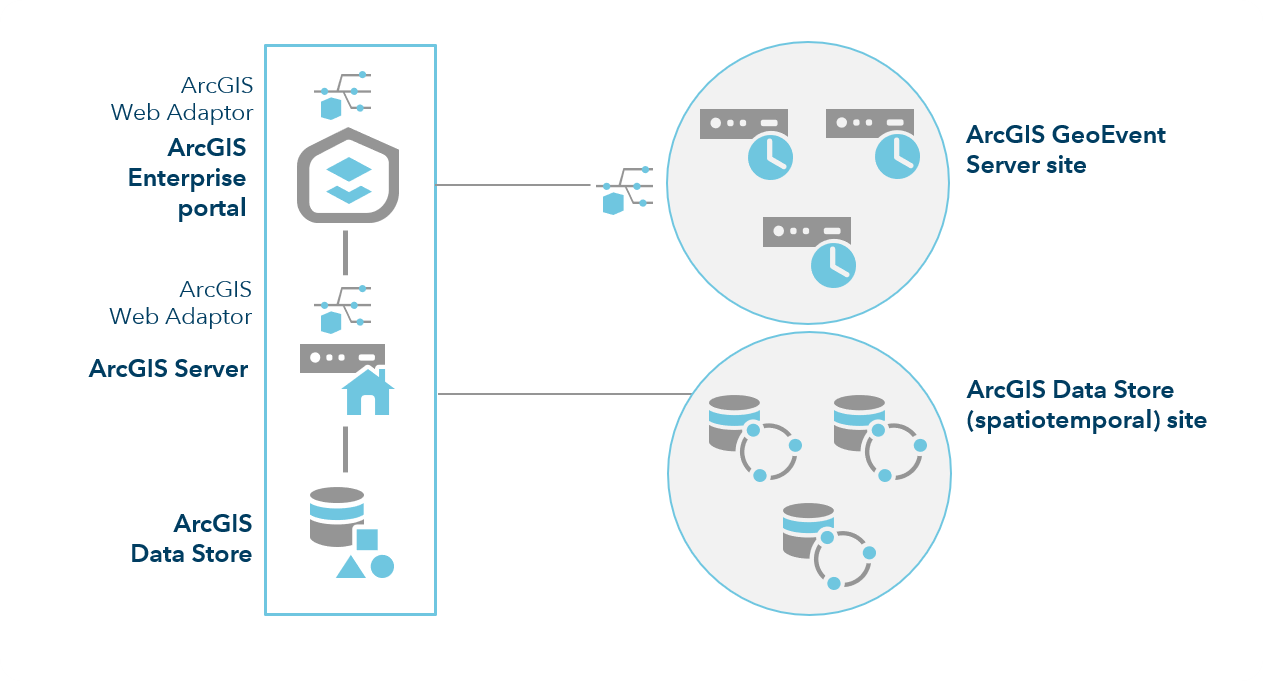
At ArcGIS Enterprise 10.6 and later, ArcGIS GeoEvent Server instances can be configured in a multiple-machine site, with the ArcGIS GeoEvent Gateway enabling distribution of resources across the machines. Setting up a multiple-machine site is typically done for one of two reasons:
- A real-time event stream is providing a higher event volume and/or event velocity than a single instance of ArcGIS GeoEvent Server can handle. Configuring a multiple-machine site distributes the event processing across the machines in the site for a highly scalable system.
- System resiliency is desired for ArcGIS GeoEvent Server. Configuring a multiple-machine site enables the ArcGIS GeoEvent Gateway to redistribute event processing if one of the machines in the site is unavailable.
ArcGIS GeoEvent Server multiple-machine sites, regardless of motivation, should be planned and implemented in collaboration with Esri Services given the complexity of the architecture.
Learn more about multiple-machine sites in ArcGIS GeoEvent Server
A minimal setup (not illustrated) in which you deploy and license ArcGIS GeoEvent Server on an existing base ArcGIS Enterprise machine is supported. However, system architects should understand the implications of system resource sharing between ArcGIS GIS Server and ArcGIS GeoEvent Server before such a solution is moved into production.
ArcGIS Notebook Server
Released at 10.7, ArcGIS Notebook Server is a complete data science platform integrated with the ArcGIS Enterprise portal.
The ArcGIS Notebook Server role enables your ArcGIS Enterprise deployment to host and run ArcGIS Notebooks. Using the Python programming language, you can perform spatial analysis, craft data science and machine learning workflows, manage GIS data and content, and automate ArcGIS Enterprise administrative tasks.
ArcGIS Notebook Server is installed on a server operating system, and is configured and federated with an ArcGIS Enterprise. An instance of ArcGIS Web Adaptor is deployed and configured with the ArcGIS Notebook Server site. At 10.7, only single-machine sites are supported.
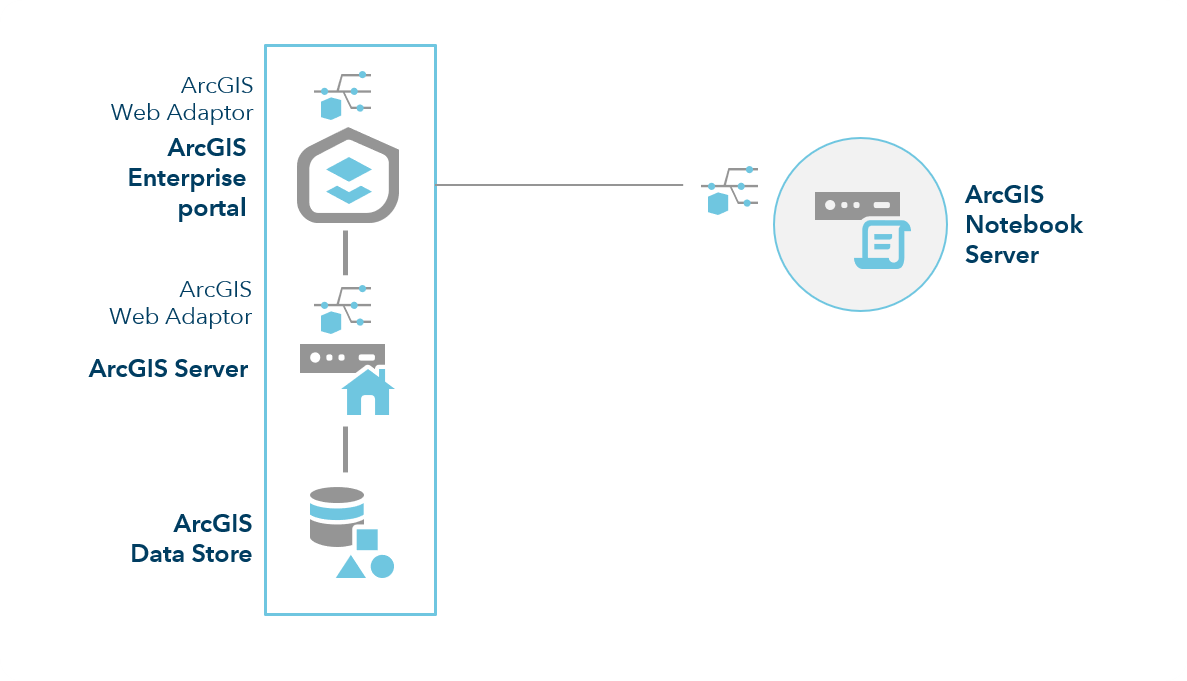
ArcGIS Notebook Server uses containers - virtualized operating systems - to provide each notebook author with their own isolated working environment and computing resources within the machine. To allocate and maintain these containers, ArcGIS Notebook Server works with Docker container software. In order for ArcGIS Notebook Server to function, Docker Engine must be installed and configured on the same machine. The complete steps to set up Docker Engine are contained in the ArcGIS Notebook Server install guide.